Does Evolution Explain All Life on Earth?
Introduction
Many kids have walked away from the faith taught by their parents after learning in school that life appeared and evolved through natural, unguided processes. Many adults have defended their atheistic faith by pointing to evolution as having examined away the need for a supernatural creator.
Is it true that science has advanced to the point where we can know for a fact that life and all its forms are just random accidents? Let's take a look at Darwin's theory of evolution in light of modern scientific discoveries.
Origin of Life
Before discussing the origin of new species, we should look at the origin of life itself. Could life have originated through purely naturalistic, unguided means, or was there an intelligent creative force involved?
Abiogenesis (Spontaneous Origin)
A longstanding theory holds that the conditions on the early Earth included the right combination of compounds in the oceans and atmosphere to react, possibly powered by electrical discharge from lightning to generate amino acids that combined to form RNA and eventually simple microorganisms.
To test this theory, a famous experiment was conducted in 1953 at the University of Chicago by a graduate student named Stanley Miller, along with his faculty advisor Harold Urey. The experiment involved simulating a lightning strike in an atmosphere of ammonia, methane, and high levels of hydrogen, which eventually resulted in the emergence of amino acids. the building blocks of proteins, necessary components of life as we know it.
The Miller-Urey experiment was touted as proof that life could have spontaneously arisen in the "primordial soup" given enough time.
Since then, however, it has become more clear that the early atmosphere would have been composed of volcanic gasses released from the Earth's mantle, comprised of concentrations of carbon dioxide nitrogen, not ammonia and methane.
If the conditions on the Primordial Earth were not favorable to the spotaneous generation of life, could the conditions have existed elsewhere and then life have made its way to Earth? That theory, known as panspermia, has been suggested as a way of addressing evidence that the conditions on the early earth were actually hostile to life.
To accept panspermia, however, still requires overcoming impossible odds for life to form. Once that happens, the microorganisms must somehow survive whatever cataclysmic event would lead to their ending up on an asteroid or comet that would makes its way to Earth, only to crash into the Earth in a tremendous fireball.
Other theories have been proposed that perhaps a chemical reaction in a geothermal vent or even ice would have been the scenario. However, in the presence of water amino acids would not spontaneously come together to form proteins, because water naturally breaks down proteins and other polymers. Even had proteins formed against all odds, would they have held together long enough in this hostile environment to form RNA, which would be highly improbable, of not impossible, even in the best of conditions, and how would that have evolved to become life?
Creation
If naturalistic processes can not explain the origin of life the only alternative is supernatural intervention.
Most religions include accounts of the origin of life. Which, if any, are true, depends on which religion, if any is true. The only religion whose truthfulness relies on historical evidence that has not been verifiably falsified would be Christianity.
Origin of Species
When Charles Darwin published his seminal work, On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection, or The Preservation of Favoured Races in the Struggle for Life in 1859, it was not the first time the idea of biological evolution had been suggested, but it did set off a revolution in thinking that eventually became the mainstream naturalistic theory of the origin of new species that is taught worldwide in schools. The question is whether, as many would suggest, the "Theory of Evolution" is a proven fact, or as many others suggest, it is still merely a theory. In fact, many have suggested that the theory has effectively been disproven. Let's dig into these two perspectives a little deeper.
Darwinian Evolution
The theory that Darwin suggested has been characterized as "natural selection" or more harshly as "survival of the fittest." Those members of a population who have characteristics that improve their survivability are more likely to reproduce and pass along those characteristics to the next generation. Over the course of many generations, especially in isolation, those adaptations become dominant and more pronounced, eventually leading from minor changes to major changes, resulting in new species. Taken over a long enough period of time, such could theoretically lead to new kinds of life entirely. Looking back over time, the theory would suggest that all life on Earth adapted from a single simple organism. It has been depicted as a "tree of life" with the branches splitting off into increasingly diverse forms of life.
Intelligent Design
The leading challenge to Darwinian evolution is known as Intelligent Design (ID). The ID theory, as applied to biology, posits that the best explanation for biological complexity is that it could only have resulted from an intelligence. Evolution can explain adaptive changes but not the origin of new complex structures or processes.
Darwin admitted the appearance of intelligent design in biology, and he suggested that it did not undermine his theory:
“To suppose that the eye with all its inimitable contrivances for adjusting the focus to different distances, for admitting different amounts of light, and for the correction of spherical and chromatic aberration, could have been formed by natural selection, seems, I confess, absurd in the highest degree...The difficulty of believing that a perfect and complex eye could be formed by natural selection , though insuperable by our imagination, should not be considered subversive of the theory.”
We must remember, though, that as scientific understanding of biology has grown since 1859, the true complexity of biological systems has been revealed to be far beyond what scientists in Darwin's time could envision. Cells are more than just blobs of protoplasm. DNA contains vast amounts of information directing the operations of complex factories utilizing intricate microscopic machinery. In addition, even some of the simplest of organisms rely on structures that are irreducibly complex.
Because intelligent design requires an intelligent designer powerful enough to create and design life, many critics dismiss the theory as creationism cloaked in a veil of science. However, before dismissing ID as pseudo-science, let's look at some of the scientific arguments from biology that present a challenge Darwin's theory.
Irreducible Complexity
In 1996, the book Darwin's Black Box: The Biochemical Challenge to Evolution was released. In it, biologist and tenured professor Michael Behe lays out his concerns with macroevolution as an explanation for the origin of complex biological structures. Citing the example of the bacterial flagellum. which bears remarkable similarity to the outboard motors used on boats, he shows both the apparent intelligent design of this structure as well as explains the irreducible complexity of the design itself.
Irreducible complexity is the argument that certain biological systems cannot have evolved by successive small modifications to pre-existing functional systems through natural selection, because no less complex system would function. In other words, the individual components or substructure of an irreducibly complex structure have no biological advantage, and even may be disadvantageous, even deadly, and thus would not be passed along through natural selection as incremental steps in the evolution of the eventual structure seen today.
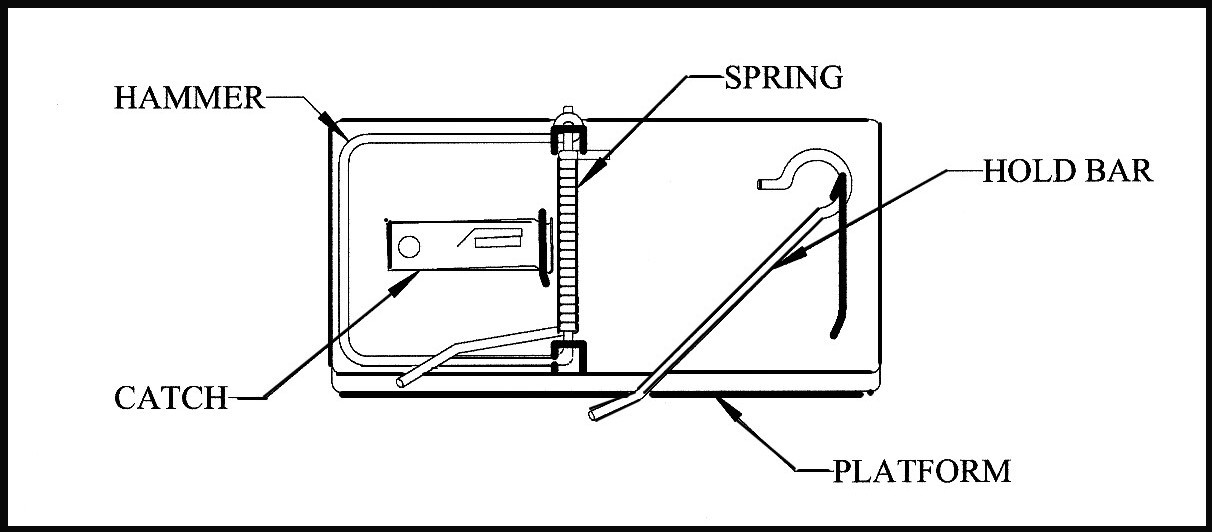
Behe uses the simple mousetrap as an example.
Micromachinery
The bacterial flagellum is not the only example of an elaborately designed system at the microscopic level in living organisms. In fact, all cells are self-contained factories comprised of micromachinery at nanoscale. Below are just a few examples.
Protein Folding
Proteins play a critical role in the inner workings of cells. In order to perform their function, they must fold into a correct 3D shape. That process alone is very complicated and requires hundreds of "chaperone" proteins that manage every detail of the process as it takes place inside the cell, which is crowded and very busy with activity.
In fact, throughout the life of a protein from it's formation in the ribosome to the point at which is it is no longer of use in the cell, the "chaperones" in the cell monitor and make adjustments to ensure the protein serves its function without interfering with other activity.
Research continues to uncover more insights into this beautifully complex process. For more information, the following article in Chemical and Engineering News provides an excellent discussion of this research: Protein folding: Much more intricate than we thought (July 31, 2017).
Turbines and Pumps
Read more in this 2021 article from Evolution News: Of Turbines and Pumps: More on Denton’s Latest.
Factories
There are many more examples of amazingly complex and sophisticated micromachines and systems which make the inner workings of a cell more like a futuristic factory than the simple view of a cell from Darwin's day. The more we learn the more astronomical the odds grow against evolution being able to explain what can be observed, especially given finite time in which to work.
Here's another one of the incredible machines at work within every cell in your body right now. Powered by ATP (mentioned above), Kinesin receives delivery instructions for cargo and then moves that cargo, sometimes enlisting help along the way, ultimately reaching the intended destination.
There are many more examples. Here's another article with good information:
A mathematician who uses statistical methods to model the fine tuning of molecular machines and systems in cells reflects…







Comments
Post a Comment